Abstract
Purpose
Patients in the Nanfang hospital with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) have had continuous survival improvement since the 2000s. To examine the main factors affecting prognosis, we conducted a retrospective analysis at a single center.
Patients and Methods
1023 evaluable patients were in this analysis (median age, 26, with a range of 14 to 73 years). The pediatric-inspired regimen, PDT-ALL-2016 regimen, was introduced in 2016, since then all patients received this treatment (N=414). While all patients between 2000 and 2015 received adult regimens (N=612). The median follow-up time for the PDT-ALL-2016 cohort was 44.7 months, and that for the adult regimen cohort was 92.9 months.
Results
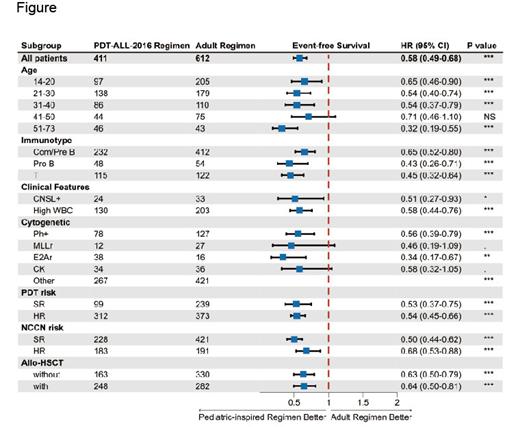
For the whole series, the 5-year overall survival (OS5y) was 57.8±5.3% in PDT-ALL-2016 cohort and 31.3±5.4%in the adult regimen cohort (P<0.001). There was no significant difference in treatment-related mortality (TRM) between the two cohorts, with rates of 11.9% and 10.6%, respectively (P=0.652). The PDT-ALL-2016 cohort showed a lower cumulative incidence of relapse (CIR) at 5-year (38.1%) compared to the adult regimen (61.1%, P<0.001). Subgroup analysis revealed that all age groups, except for patients aged 41-50 years (HR=0.77, 95% CI, 0.48-1.21, P=0.251), can benefited from the PDT-ALL-2016 regimen. Notably, the older patients subgroup (50-73 years old) showed a significant improved outcome within the PDT-ALL-2016 cohort, compared with adult regimen cohort (HR=0.3, 95% CI, 0.17-0.54, P<0.001). Within this subgroup, CIR and TRM were 44.9% vs. 75.1% (P<0.001) and 4.3% vs. 12.1% (P=0.196), in PDT-ALL-2016 cohort and adult regimen cohort, respectively. Furthermore, subgroup analysis indicated that both high-risk and standard-risk patients had better outcome in the pediatric-inspired regimen cohort. For the HR group, OS5y were 25.1±6.3% vs. 55.5±6.1% (P<0.001), and EFS5y were 18.8±5.8% vs. 43.1±5.9% (P<0.001) in two cohorts. Patients who underwent allo-HSCT could also benefit from PDT-ALL-2016 regimen. For this subgroup, OS5y were 47.7±7.1% vs. 67.7±6.1% (P<0.001), and EFS5y were 37.2±6.7% vs. 53.9±6.7% (P<0.001) in adult regimen cohort and PDT-ALL-2016 cohort, respectively.
Conclusion
For adult ALL patients, compared with adult regimen, pediatric-inspired regimen resulted in significant improved outcome in all age and risk groups, as well as in patients who underwent allo-HSCT.
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(NFSC82170163, 81970147), Clinical Study of Nanfang Hospital(LC2016ZD009/2019CR012).
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.